In 2023, your website is likely the foundation of your digital marketing efforts — and a beautifully designed, technically sound website is something you should be proud of. But launching a website is just the beginning of building a strong digital presence.
Ongoing content marketing strategies can help you keep your website fresh while improving brand awareness and boosting organic search traffic. When you deeply understand your target audience on an analytical level, you can continuously craft content that attracts your ideal buyers and guides users through your sales funnel.
If you’re eager to learn more about content marketing, a great place to start is learning the lingo. We love content marketing, and we completely understand that it can be an intimidating tactic to learn about and navigate. We’re here to share what we’ve learned. Here are some of the most useful content marketing terms we use and what they mean.
Content Marketing Techniques and Definitions
Here’s a list of the most common content marketing techniques and terms, broken into a few categories:
1. Content Marketing Terms
- Content Marketing
- Buyer’s Journey
- Buyer Personas
- Calls-to-Action (CTA)
- Content Funnel
- Top of Funnel
- Middle of Funnel
- Bottom of Funnel
- Content Gap Evaluation
- Drip Campaigns
- Landing Page
- Split Testing
- User Experience (UX) Design
2. SEO Definitions
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Search Engine Results Page (SERP)
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
- Keyword
- Short-Tail Keyword
- Long-Tail Keyword
- Keyword Research
- Keyword Stuffing
- Meta Description
- Noindex
- Backlinks
3. Types of Content
- Article Content
- Cluster Hub
- Dynamic Content
- Listicle Articles
- Pillar Page
- Single Intent Articles
- Thought Leadership Articles
- Evergreen Content
- Downloadable Content
- Case Studies
- Demos
- eBooks and Guides
- Market Reports
- Templates
- Use Cases
- Webinars
- White Papers
- Gated Content
4. Success Metrics
- Bounce Rate
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversions
- Conversion Rate
- Domain Authority
- Engagement Rate
- Impressions
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Pageviews
- Page Authority
- Sales Revenue Attribution Models
- Site Audit
- Time on Site
- Unique Visitors
- Users
- Website Traffic
- Direct Traffic
- Organic Traffic
- Paid Traffic
- Referral Traffic
Content Marketing Terms
Content Marketing:
Content marketing is a digital marketing strategy that utilizes the content on your website to attract and guide users along their buyer’s journey from initial discovery to conversion.
Buyer’s Journey:
A buyer’s journey outlines the series of events a customer takes when making a specific purchase. The buyer’s journey typically follows a predictable sequence: problem identification, research, evaluation, and vendor selection. Developed using customer research — including analytics, customer interviews, and questionnaires — the buyer’s journey is the foundation of a strong, well thought-out content funnel. Learn more about buying insights and the buyer’s journey in our post, How to Decode Your Customers’ Purchasing Habits and Preferences.
Buyer Personas:
Buyer personas represent segments of your target audience(s) based on customer research. These personas help marketers and sales teams visualize who they’re targeting with content and understand their needs. If you’re interested in drafting a buyer persona for your target audience, check out our blog post, How to Create B2B Buyer Personas.
Call to Action (CTA):
A call to action prompts website visitors to take an immediate, specific action. Websites that drive sales typically have a strategically varied group of calls to action that target buyers in different phases of the buyer’s journey. Calls to action can be designed to increase time on site, or drive lead conversions.
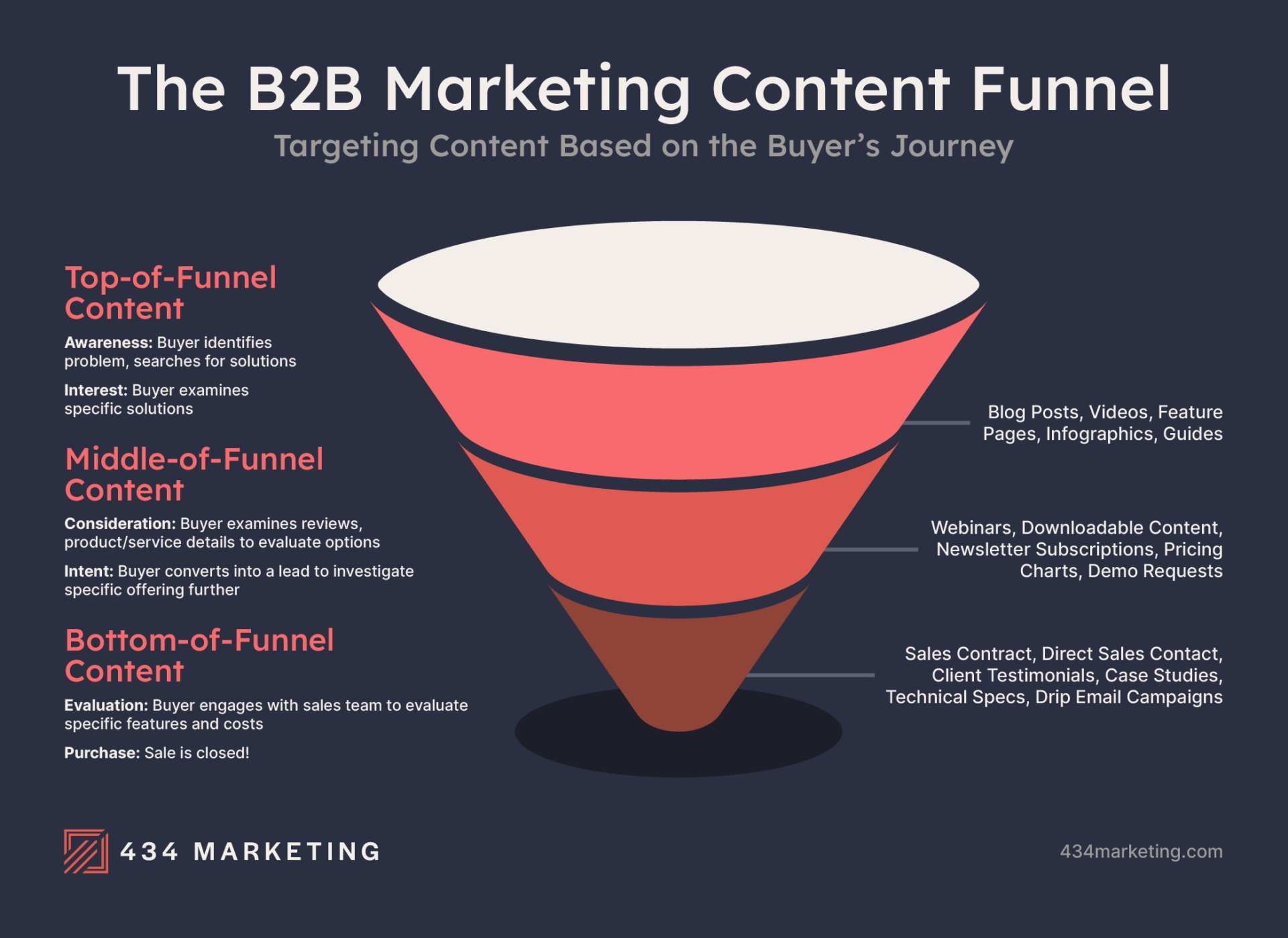
Content Funnel:
Similar to a traditional sales funnel, the content funnel organizes content into three categories — top of funnel, middle of funnel, and bottom of funnel — based on how mature a lead is. If you’d like to learn more about our process for perfecting a website’s content funnel, read our guide, How to Balance Your Business’ Content Funnel.
- Top of Funnel (ToFu): Top-of-funnel content attracts buyers in the initial phases of the sales funnel, when they become aware of a need and begin researching solutions. Top-of-funnel content addresses broader, informative topics that capture the attention of your target audience by answering questions about the problems they want to solve.
- Middle of Funnel (MoFu): Middle-of-funnel content is geared toward buyers that are evaluating the products or services available to meet their needs. Middle-of-funnel content aims to convert passive website visitors into leads that marketers and sales teams can continue to target and warm up through drip campaigns and direct outreach.
- Bottom of Funnel (BoFu): Bottom-of-funnel content targets buyers in the final phase of the buyer’s journey. Creating effective bottom-of-funnel content is critical in differentiating your business from the competition with unique value propositions, client success stories, and data that emphasizes why your offering is superior.
Content Gap Evaluation:
During a content gap evaluation, market researchers analyze a website’s digital acquisition channels to identify strategic content opportunities that will attract leads to your brand. Content gap evaluations often involve comparison of one brand’s strategic performance with competitors.
Drip Campaign:
A drip campaign is a set of automated emails that are designed to help sales teams warm up leads without investing in direct outreach. Drip campaign emails are usually scheduled on a timeline, or are organically prompted when a user takes a specific action, such as clicking on a link, downloading a resource, or looking at a webpage. When paired with content marketing, drip campaigns can be particularly powerful — if a lead’s information is captured on, say, a piece of gated content, you can craft an entire drip campaign that will automatically trigger and gradually warm that lead.
Landing Page:
Landing page content drives conversions. Landing pages highlight a single call to action and compel site visitors to exchange personal contact information — name, email, phone number — for an offer, such as an informative eBook or report.
Split Testing:
Split testing — also known as A/B testing — is an effective way to optimize a piece of content. Visitors are randomly shown a variant of the content (either version A or version B), which allows marketers to compare the two variants based on engagement, click-through rate, and other end-point actions.
User Experience (UX) Design:
User experience designers systematically examine traffic flow, website user behaviors, targeted audience content preferences, and sales objectives to increase time on site and prompt lead conversions.
SEO Definitions
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Search engine optimization helps improve a webpage’s organic position on a search engine results page. Search engine optimization involves numerous tactics, ranging from keyword analysis to content optimization, meta descriptions, and internal linking.
Search Engine Results Page (SERP):
Search engine results pages pop up when you enter a query into a search engine. Content marketers aim for content to rank as highly as possible on SERPs to catch potential customers’ attention as quickly as possible.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM):
Search engine marketing involves using paid advertisements, such as pay-per-click ads, to drive traffic to a webpage. SEM involves B2B and B2C sellers submitting “bids” for ad space on certain pages and can be quite costly.
Keyword:
A keyword is a word or phrase that appears with a specific level of frequency in a piece of web content. Search engines use keyword appearances to rank how relevant and useful a piece of content is based on a user’s search query. Keywords can be short-tailed, or long-tailed.
- Short-Tail Keyword: Short-tail keywords address broad topics and contain 1-3 words. Short tail keywords generate more traffic than long tail keywords because they are less specific and are searched more frequently. Short-tail keywords can help develop domain authority, thanks to higher traffic on the site, but these audiences are often less likely to convert.
- Long-Tail Keyword: Long-tail keywords reflect phrases that your target audience is searching for. They are typically specific and detailed, and sometimes are posed in the form of a question. Long-tail keywords are effective at reaching audiences that are interested in your specific offering, but generally see a lower search volume than broader short-tail keywords.
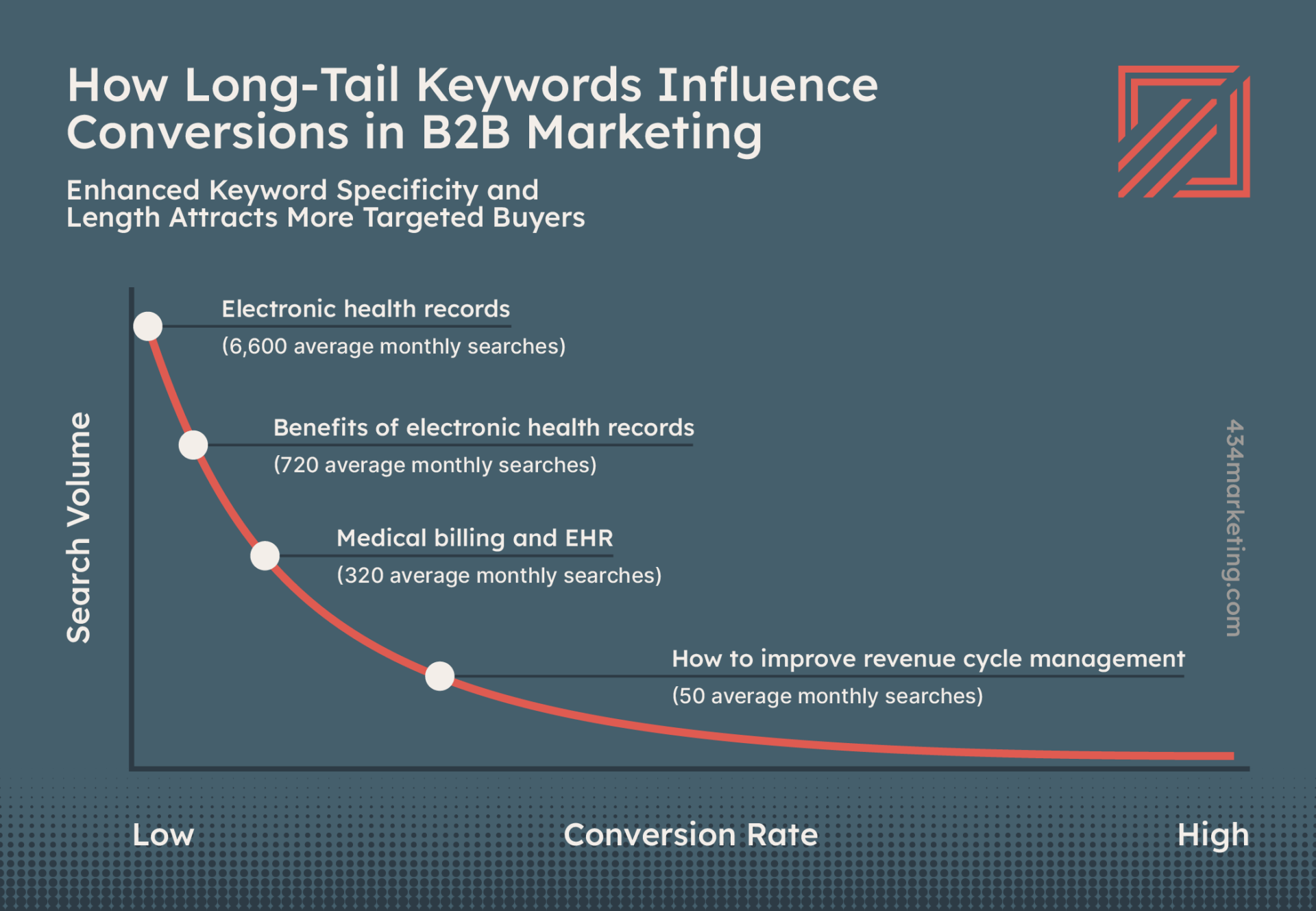
Keyword Research:
Keyword research is the process of identifying and evaluating search terms that align with your content marketing strategy. Typically, keyword research is conducted using various tools that aggregate data across numerous search engines.
Keyword Stuffing:
Have you ever read a blog post that used the same word or phrase so often that it confused the article’s meaning? That’s keyword stuffing, and it’s not an effective way to ensure your content ranks highly for a keyword — and search engines don’t look kindly on this tactic. If you use keywords in a way that Google deems is misleading, your domain can be penalized significantly. A good rule of thumb is to use a keyword once per 200 words of copy to avoid keyword stuffing.
Meta Description:
A meta description is an element that describes what a visitor can expect to find on a webpage, and helps search engines index pages. Meta descriptions are the snippets of text that show up on SERPs so users can evaluate the relevance of a site beyond the headline. Note: While plugins like Yoast can help you flag to search engines what you want displayed as your meta description, sometimes the algorithm will favor a different snippet that lives within your content.
Noindex:
Noindex tags block search engines from indexing content. Using noindex tags prevents certain content — such as specific offer pages or gated content — from ranking on search engine results pages.
Backlinks:
Also referred to as “inbound links,” backlinks are links from another website to your website. Gaining backlinks from high-authority domains can improve your website’s search engine rankings.
Types of Content
Article Content:
Web articles or blog posts can vary in length and address content topics that align with your brand, but aren’t part of your website’s core navigational structure. Here are some key article formats that we use regularly at 434 Marketing:
- Cluster Hub: A cluster hub summarizes and connects topical content together in a succinct, sectioned article or page that helps users navigate to downstream content. By grouping content together, you can provide a better user experience while reaping technical SEO benefits.
- Dynamic Content: Dynamic content is adaptive and changes based on who is visiting your webpage, and where they are in the buyer’s journey. For example, warmed-up leads who visit your site will subsequently be directed toward more bottom-of-funnel content.
- Listicle Articles: A listicle is a helpful, informative article that takes a list-based format. Listicles are effective at breaking down complex offerings into digestible, headlined sections, so visitors can better focus on the specific information they need.
Pillar Page: A pillar page provides a broad overview of a topic and are important vehicles for integrating long- and short-tailed keywords. Cluster hubs direct traffic to internal pillar pages. - Single-Intent Articles: A single-intent article is a focused piece of content that targets a specific audience with a specific question or concern. These articles pose a great opportunity for integrating long-tail keywords.
- Thought Leadership Articles: Thought leadership content demonstrates expertise and market knowledge on a topic that’s relevant to your buyers. Thought leadership articles may be ghostwritten for a business leader, and typically draw insights from an in-house subject matter expert.
- Evergreen Content: Evergreen content ages well and doesn’t require regular maintenance. Evergreen content addresses topics that are highly relevant to your target audiences, but are not time sensitive, seasonal, or linked to specific events.
Downloadable Content:
While articles attract traffic, downloadable content converts site visitors into leads via landing pages. Downloadable content expands on topics addressed in articles and provides prospects with more detailed and valuable insights.
- Case Studies: Case studies highlight a real customer’s positive experience with your brand. Case studies follow a predictable format: an overview of the challenge, the solution, and the impact. Case studies are a form of bottom-of-funnel content that can convert buyers in the evaluation phase of the buyer’s journey.
- Demos: Product demos guide a prospective buyer through the features and benefits that a solution offers. Offering pre-recorded, on-demand demos or live, sales-guided demos are great ways to engage with prospective buyers while they evaluate solution options.
eBooks and Guides: eBooks and guides are self-published resources that expand on a topic that appeals to a brand’s target audience. eBooks establish a brand’s expertise in a market area. - Market Reports: Market reports highlight original data insights that brands have gleaned.
- Templates: Templates are a way to share best practices and helpful how-to sheets with prospects.
- Use Cases: A use case explains how prospects benefit from using your solution to achieve a specific goal. Use-case content helps brands appeal to segmented audiences based on distinct applications while diving into details, such as product documentation and standard operating procedures.
- Webinars: Both live and on-demand webinars are highly effective lead generating tools. Make sure to select an attention-grabbing topic that will be informative and engaging for your target audience.
- White Papers: White papers use a persuasive, academic format to help a prospective buyer evaluate an issue relating to their business objectives. Whereas case studies highlight real-life customer scenarios, white papers draw on technical information, forecasts, and well-sourced data to build credibility within your target audience.
- Gated Content: Gated content refers to downloadable content that is “gated” by a landing page. Prospects need to convert into leads by exchanging contact information for a valuable piece of content.
Success Metrics
Bounce Rate:
Bounce rates depict instances when a user visits a page and leaves without interacting with the site or navigating to another page. A high bounce rate usually means that a search engine misinterpreted your content’s relevance to a particular search query, or that your content simply didn’t catch your visitor’s attention.
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
A click-through rate reflects the percentage of link clicks per overall impressions. CTRs help marketers gauge how well call-to-action links and inbound links are performing.
Conversion:
Conversions vary based on certain business objectives and calls-to-action. One marketer might define a conversion as a point when a site visitor fills out a form and converts into a lead, whereas another may deem a conversion as a purchase.
Lead Conversion Rate:
A lead conversion rate measures the ratio of leads captured compared to overall website visitors.
Domain Authority:
Domain authority scoring predicts how likely a website is to rank on a search engine results page. Domain authority scores are based on a combination of quality, subject matter relevance, popularity, and backlinks. Algorithms that determine domain authority are constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay informed of these changes and revise strategies and content regularly.
Engagement Rate:
Engagement rates measure content interactions — likes, clicks, comments, and shares — on social media platforms. It is a good indicator of content relevancy and popularity.
Impressions:
Impressions measure the overall volume of views earned by a piece of content.
Net Promoter Score (NPS):
The net promoter score is a popular way to predict future revenue growth by evaluating how likely customers are to recommend your business. A high NPS can also be a positive selling point for prospects who want to prioritize good customer service.
Pageviews:
Pageviews are counted each time a web page is loaded in a browser, including duplicated visits from the same user. Unique pageviews indicate how many people looked at a web page.
Page Authority:
Similar to domain authority, page authority scores help marketers evaluate how likely a webpage will rank highly on a SERP.
Sales Revenue Attribution Models:
Sales revenue attribution models help marketers measure the true impact of marketing campaigns on sales. Learn more about revenue attribution models on our blog.
Site Audit:
Site audits use web crawlers to identify any errors and warnings on a website. Broken links, sluggish page loading, and missing meta descriptions can all harm a website’s position in search results. Site audits should be performed regularly to ensure that errors and warnings are quickly addressed.
Time on Site:
Time on site measures the seconds that elapse between a site entrance and exit, and it’s a good indicator of overall content engagement, messaging strategy, and site performance. Effective UX design increases time on site by targeting users with relevant, compelling content, or drives conversions through CTAs.
Unique Visitors Per Month (UVPM):
The unique visitor per month metric counts how many times someone visits your website, without counting duplicate visits. UVPM is a reliable way to gauge general interest in your website content, because it won’t track new sessions each time someone from your internal team checks on a webpage.
Users:
Website users reflect individual IP addresses that access a website. Google will segment users into new and returning users, and can also provide demographic data, site behavior, and other important information to better understand who is visiting your site.
Website Traffic:
Website traffic counts overall site visits, or sessions, broken into four categories based on the traffic source:
- Direct Traffic: Direct traffic measures how many visitors entered your site via a URL that they entered into their browser or accessed via a bookmark.
- Organic Traffic: Organic traffic is referred by search engines and measures how many times a search query directed a visitor to your website.
- Paid Traffic: Paid traffic reflects the amount of site visits that resulted from a digital advertisement.
- Referral Traffic: Inbound links from emails, texts, direct messages, social media content, and external websites all drive referral traffic.
Content marketing done right can drastically increase your digital footprint, and we’re here to help.
At 434, we understand how to use data-backed content marketing strategies to drive growth in leads and revenue for our clients. Every content marketing decision we make aligns with our clients’ business objectives.
If you’re ready to overhaul your marketing strategy — and you recognize that we know what we’re doing — contact us. We’d love to share more about how to supercharge your marketing efforts.